
Whole-body networks: a holistic approach for studying aging
We showed that the architecture of the whole-body network changes with aging. We also found that it correlates with verbal learning and short-term me
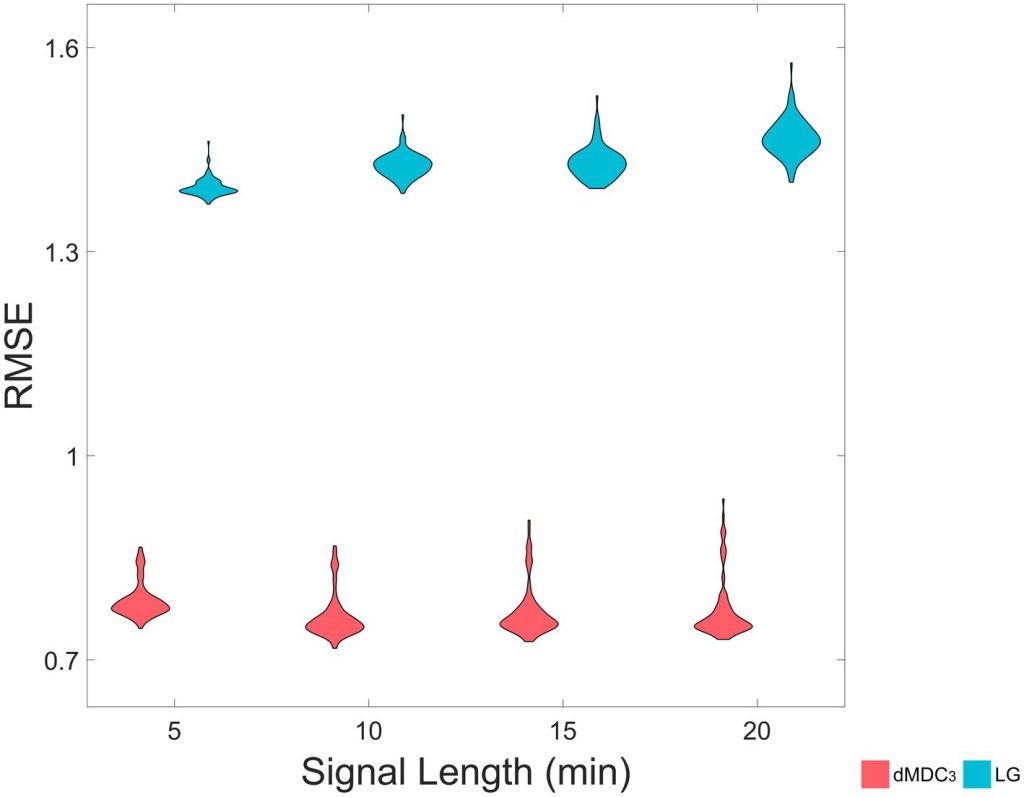
Multiscale detrended cross-correlation coefficient: estimating coupling in non-stationary neurophysiological signals
We introduced the Multiscale Detrended Cross-Correlation Coefficient (MDC3), a novel and more accurate method for estimating functional connectivity in non-stationary signals like EEG, MEG and fMRI.
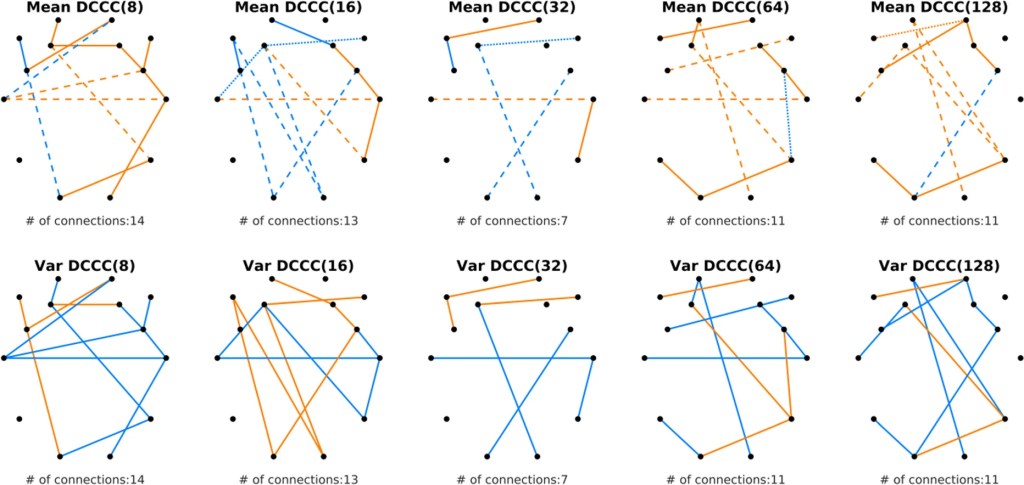
Fingerprints of Decreased Cognitive Performance on Fractal Connectivity Dynamics in Healthy Aging
Here we explore the detrended cross-correlation coefficient (DCCC) of young and elderly EEG. Differences can be seen across the whole cortex, but most importantly across several temporal scales. DCCC was also associated with cognitive performance.
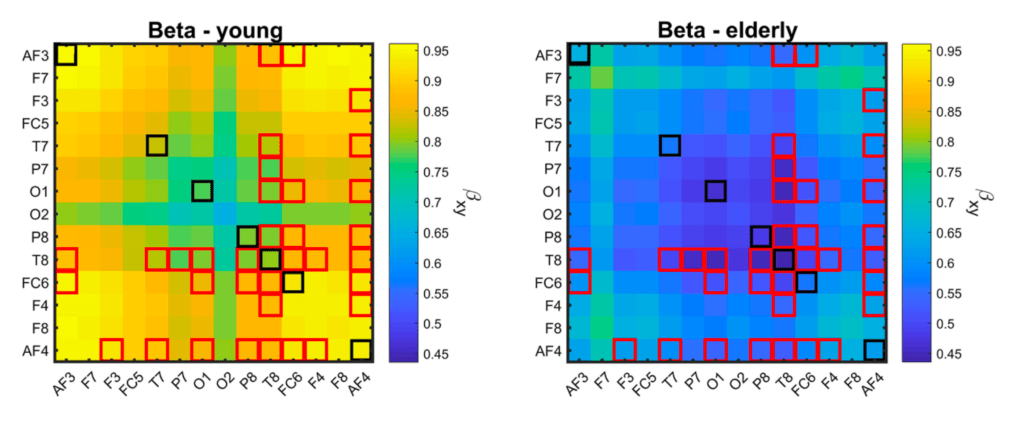
Resting-State Fractal Brain Connectivity is Associated with Impaired Cognitive Performance in Healthy Aging
Using multiple-resampling cross-spectral analysis we separated the oscillatory and scale-free components of the auto- and cross-spectral exponents (βxy) of resting-state EEG. The results show that βxy of several regions and connections decreases during aging. βxy is also associated with impaired cognitive performance.
Scale-Free Functional Brain Networks Exhibit Increased Connectivity, Are More Integrated and Less Segregated in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease following Dopaminergic Treatment
In our latest paper we explored how the multifractal functional connectivity changes after dopaminergic treatment (DT) in Parkinson’s patients. We found that after DT the constructed networks are more connected, more integrated and less segregated. We also found that verbal intelligence correlates with the small-worldliness of scale-free brain networks.
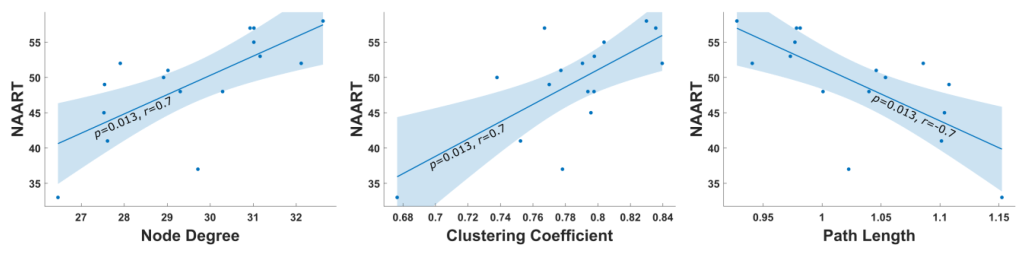
Real-Time Estimation of Nonstationary Coupled Dynamics
Recently we started using the detrended cross-correlation coefficient for the estimation of nonstationary coupled dynamics. We decided to make a fast and efficient real-time implementation of it.
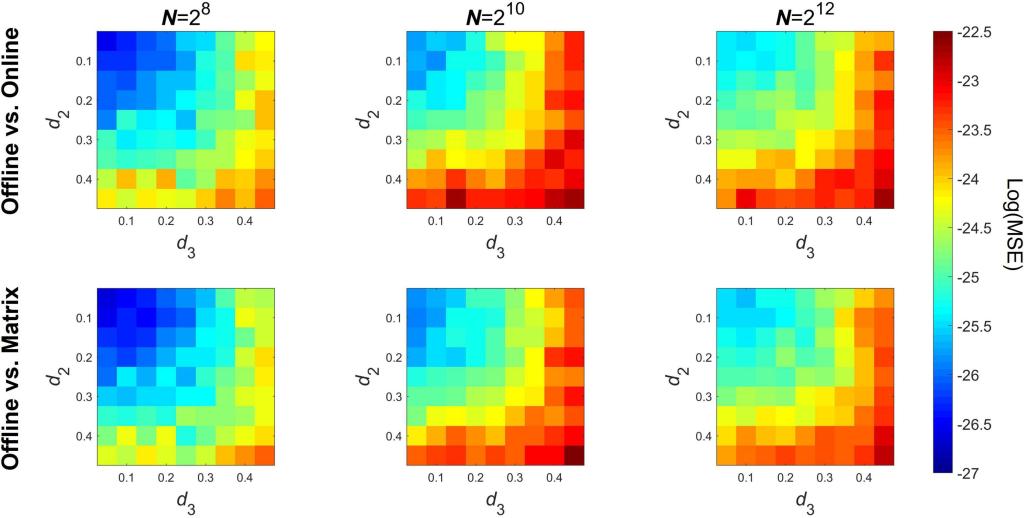
Separating scale-free from oscillatory components in coupled dynamics
Multiple-Resampling Cross-Spectral Analysis (MRCSA) is the bivariate extension of Irregular Resampling Auto-Spectral Analysis (IRASA). In this publication we show that MRCA is capable of isolating the different components of the EEG signal.

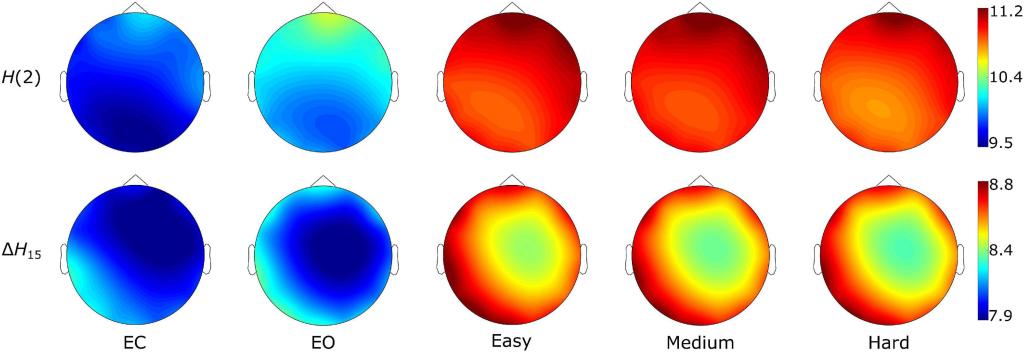
Effect of visual pattern recognition task in multifractal brain networks
The strength of multifractal connections changes during a visual pattern recognition task. Even if the task difficulty was proven by differences in the success rate and reaction time, the multifractal functional connectivity did not differ between the three task states.
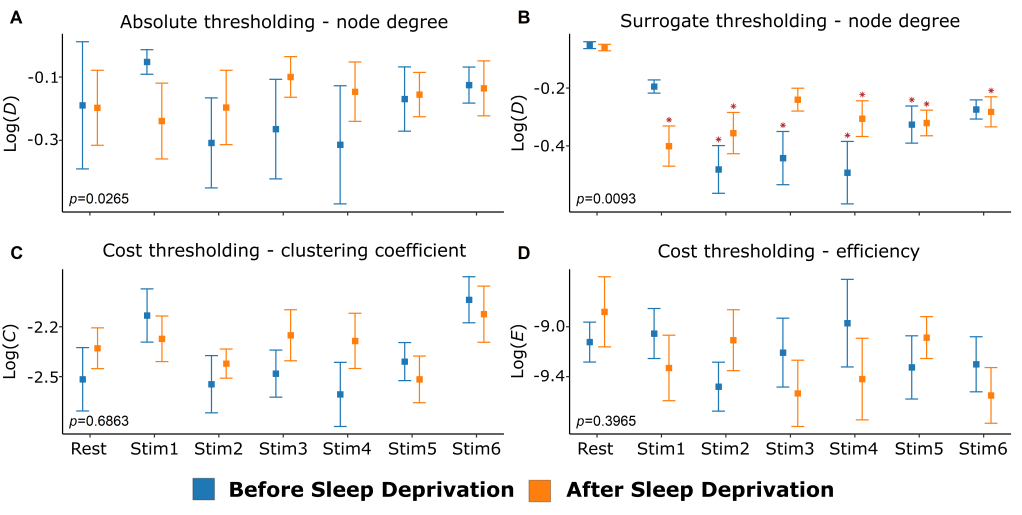
Effect of motor task in brain networks
The brain connectivity decreases during a finger tapping task, similarly to previous n-back studies. While this might seem counterintuitive it could mean that unnecessary connections are being pruned for better task performance.
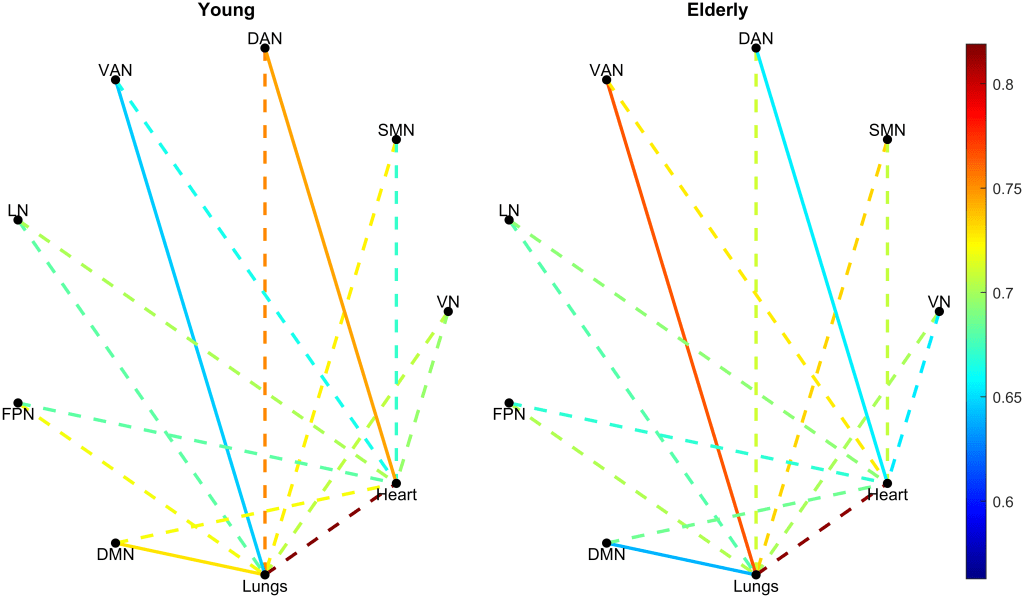
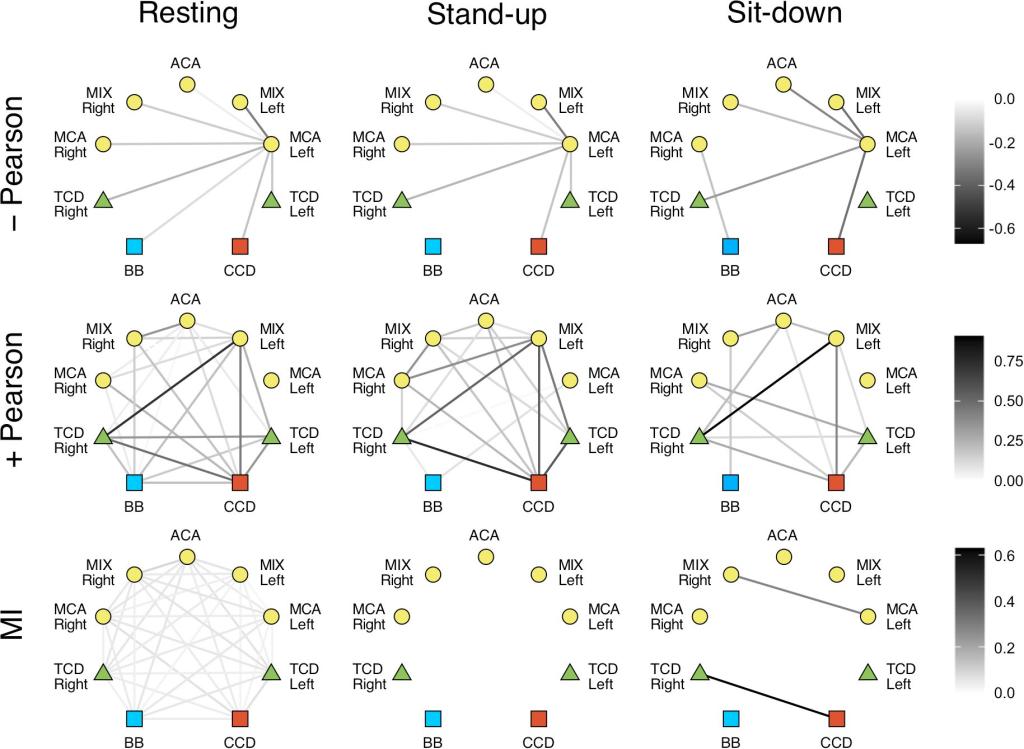
Cardio-respitatory-cerebral network
The architecture of cardiorespiratory-cerebrovascular networks shifts when standing up. This change is especially prominent in the non-linear coupling (MI: mutual information).
Schizophrenia: Changes in fractal component
The schizophrenia-related changes on the EEG is found only in the fractal component of the power spectrum.
